Different Bites
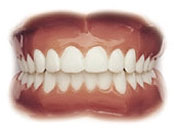
Ideal
All the teeth contact each other properly in the correct vertical and horizontal relationship.
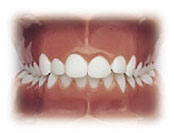
Posterior Crossbite
Posterior crossbites usually result from a constricted upper jaw or unusually wide lower jaw. A narrow upper jaw will often force a patient to move their lower jaw forward or to the side so that they are able to find a stable bite. When closed into this accommodated position, the lower teeth are located outside the upper
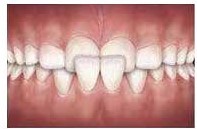
Anterior Crossbite
Anterior crossbites usually arise from excessive crowding. As there is insufficient space for the tooth to erupt into its ideal position, the tooth will find another place to come in. An anterior crossbite can result from an upper tooth positioned closer to the palate or a lower tooth positioned toward the lower lip.
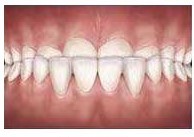
Underbite
When the lower front teeth are positioned in front of the upper teeth an underbite is present. This can result from dental (reverse positioning of the teeth) or skeletal (discrepancy of jaw sizes) reasons, or a combination of both.
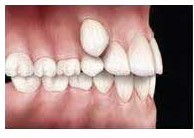
Abnormal Eruption
A tooth erupts into an abnormal place as it is inhibited from growing into its proper position. This typically results from retained primary (baby) teeth which have not exfoliated (come loose and fall out) as it normally would or from excessive crowding.
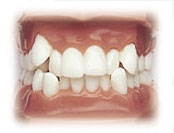
Crowding
Crowding of the teeth is the most common orthodontic problem. Although many factors contribute to dental crowding, this problem is usually inherited and stems from a discrepancy between available space in each jaw and the size of the teeth. Aside from aesthetic considerations, poor alignment of teeth may be associated with periodontal problems and an increased risk of dental decay due to difficulty in maintaining optimal oral hygiene.
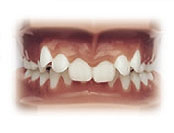
Deepbite
Excessive vertical overlapping of incisor teeth, called “overbite”, is generally found in association with a discrepancy between the length of the upper and lower jaws. It usually results in excessive eruption of either the upper or lower incisors or both. Associated problems may include excessive display of gum tissue, biting the roof of the mouth and incisor wear.

Deepbite
Excessive vertical overlapping of incisor teeth, called “overbite”, is generally found in association with a discrepancy between the length of the upper and lower jaws. It usually results in excessive eruption of either the upper or lower incisors or both. Associated problems may include excessive display of gum tissue, biting the roof of the mouth and incisor wear.
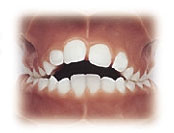
Openbite
A lack of vertical overlap of the incisor teeth can usually be traced to jaw disharmony or persistent habits (i.e. digit sucking habits or posturing of the tongue between the front teeth) or excessive vertical growth of one or both jaws. In these situations, the front teeth do not overlap at all. Early assessment and intervention with these disorders is critical to the overall success of treatment.
Spacing
Spaces between teeth are another common problem associated with the need for orthodontic care. Like crowding, spacing may be related to a tooth-to-jaw-size disharmony. Incisor protrusion and fremuns (gum tissue attachments that connect the lips to the jaws) are also a common causes of spacing between the upper front teeth. Other contributing factors include atypical or unusually narrow teeth, and missing or impacted teeth.
Crowded Teeth
Crowded teeth or overcrowding takes place when the jaw bone is too small for teeth to grow into the mouth on a straight trajectory. As a result, the teeth need to rotate and overlap against each other to fit in, creating crookedness and malalignment.


Irregular teeth shape or size issues
Like a jigsaw puzzle, teeth needs to be in a certain shape and size to have the best fit against each other.


Open Bite
An open bite occurs when the front upper and lower teeth slant in an outward direction, preventing them from touching each other when the patient bite down.


Under Bite
An underbite happens when the teeth along the lower jaw protrude out farther than the upper front teeth. It’s usually a result of incorrect jaw alignment.


Over Bite
An overbite is evidenced when the upper jaw and teeth are extend too far over the teeth on the lower jaw resulting in the appearance of protrusive upper lip and teeth, or buck teeth. Overbite is the result of a mismatch in the size between upper and lower jaw bone sizes, with an abnormally small lower jaw bone being the most common.


Crossbite
A crossbite occurs when a tooth (or several teeth) is situated too close to the cheek or tongue than the tooth it should align with in either the upper or lower jaw. As a result, the teeth involved in the crossbite are not able to bite against each other normally, creating an interference in the bite during chewing.


Highly Complex Cases
A deep bite occurs when there is too much overlapping between the top and bottom front teeth.


Book a Consultation
Get started today by calling us at (604) 474-1141, or by booking a consultation.
During your initial consultation, we will understand your situation, perform a visual examination of your bite, recommend a treatment plan and answer any questions or concerns you may have.
Innova Orthodontics
Monday
Closed
Tuesday
10:00am – 6:00pm
Wednesday
8:30am – 5:00pm
Thursday
8:30am – 5:00pm
Friday
7:30am – 3:00pm